Outside AIDA model
Did you know there is more to decision-making than the widely known AIDA (Attention, Interest, Desire, Action) marketing model? Decision-making is a nuanced psychological process influenced by multiple cognitive, emotional, and social factors. Understanding this process can profoundly enhance marketing strategies by revealing how consumers think, feel, and act.
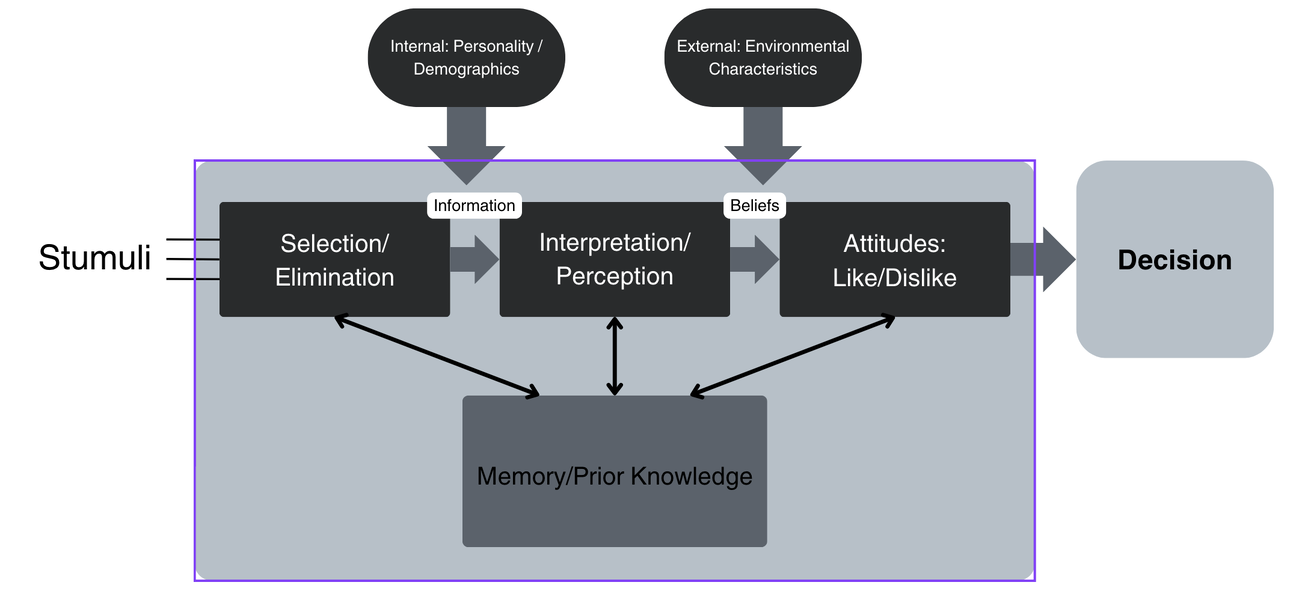
1. Stimulation and Selection: Capturing Attention
The decision-making journey begins when consumers encounter various stimuli from their environment—ranging from everyday purchases to major life decisions. At this stage, individuals selectively focus on stimuli they perceive as relevant or significant. For marketers, understanding what captures consumer attention is crucial. Creating targeted, relevant stimuli ensures your marketing efforts resonate and stand out amidst the noise.
2. Information Processing: The Role of Internal Factors
Once a stimulus captures attention, the cognitive process of information processing begins. Internal characteristics such as personality traits, demographics, cognitive styles, and emotional states significantly influence this phase. Memory and prior experiences shape consumers’ expectations, perceptions, and evaluations. Marketers should personalize messaging to align closely with their target audience’s internal attributes and past experiences, increasing resonance and effectiveness.
3. Interpretation and Perception: Constructing Meaning
During interpretation, consumers construct meaning from the information received, guided by cognitive biases and emotional responses. Beliefs shaped by cultural, social, or familial influences further impact perception. Marketers must be aware of these diverse influences and craft messaging that acknowledges or strategically navigates consumer biases and beliefs to positively shape perceptions.
4. Attitude Formation: Developing Preferences
As information is interpreted, attitudes form based on consumers’ evaluations—positive or negative—towards products, brands, or ideas. External environmental factors and societal norms heavily influence these attitudes. Brands must actively manage their image, emphasizing positive aspects and addressing potential negative perceptions, thereby strategically guiding consumer preferences.
5. Decision-Making: Integrating the Influences
The final decision represents the integration of cognitive processing, emotional influences, attitudes, and external societal factors. Consumers evaluate options, weighing advantages and disadvantages before arriving at a choice. Effective marketers provide clear, compelling reasons why their offering stands out, simplifying the decision-making process for consumers.
Practical Advice for Marketers:
- Clearly define and strategically deliver relevant stimuli to capture consumer attention effectively.
- Leverage demographic and psychographic insights to personalize communication, addressing internal consumer characteristics.
- Address cognitive biases and emotional drivers to positively shape consumer perception.
- Regularly evaluate and manage brand attitudes by aligning marketing efforts with consumer values and societal norms.
- Make consumer decisions simpler by clearly communicating unique benefits and differentiators of your offering.
Understanding the psychological underpinnings of decision-making can empower marketers to craft more precise, effective, and resonant campaigns, ultimately driving consumer action and brand loyalty.
Leave a Reply